
| Common apparatus |
|---|
| Hydraulic system |
| Electronic components |
| Data acquisition |
| EMG monitoring |
| NLID Tools |
| Troubleshooting |
| Materials |
| Supine apparatus |
|---|
| Assembly procedure |
| Safety Measures |
| Components |
| Servovalve |
| Actuator |
| Potentiometer |
| Pressure Filter |
| Torque transducer |
| Boot |
| Literature |
| Computing resources |
|---|
| CVS |
| Ethics |
|---|
| SDS / Inventory |
|---|
Potentiometer calibration - supine
Objective
Obtain a potentiometer module signal sensitivity of 10 V/rad (or 0.1 rad/V) by setting the gain of the potentiometer module.
According to the potentiometer manufacturer's specs, the device provides a nominal 346 degree travel range. Since this is not exact, it cannot be used to accurately determine the potentiometer's natural sensitivity; a calibration must be performed.
Method
- Trim the potentiometer module gain to 2. (Any known low value will do -- though a gain of 1 is not achievable on the pot module.)
- Determine the current static sensitivity of the pot/pot-module combination. A 21-point curve of the actuator angle vs. module output was determined (black markers and curve.) A precise Mitutoyo goniometer was used to measure the angle. A X12 magnifying glass was used to read the ruled scale. The slope of the resultant calibration curve indicates a potentiometer sensitivity of 3.374 = 6.7482/2.
- Adjust the pot-module gain to 2.964 = 10/3.374 to obtain the overall desired pot/module sensitivity.
- Re-do the calibration, as in step 2, to confirm the sensitivity setting (magenta markers and curve.)
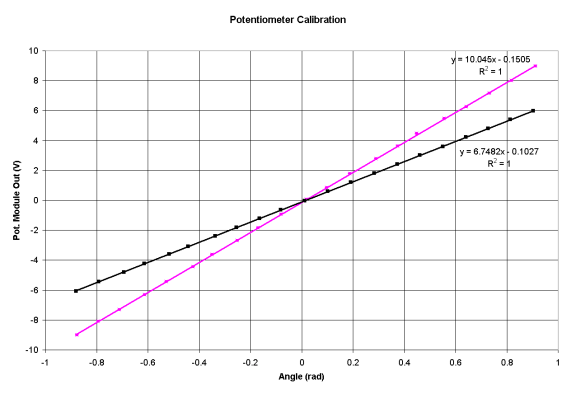
Note that the offset in the calibration curve is not that important. The servo controller takes this offset into account at startup. Also, the offset will change when the helical coupling is loosensed and tightened during maintenance.
History
2001-12-12: Calibration regression equation: y = 10.03x - 0.0705; R^2 = 0.9999
2004-06-08: Calibration regression equation: y = 10.045x - 0.1505; R^2 = 1
Last modified: Jun 8, 2004 Ross Wagner