
| Common apparatus |
|---|
| Hydraulic system |
| Electronic components |
| Data acquisition |
| EMG monitoring |
| NLID Tools |
| Troubleshooting |
| Materials |
| Supine apparatus |
|---|
| Assembly procedure |
| Safety Measures |
| Components |
| Servovalve |
| Actuator |
| Potentiometer |
| Pressure Filter |
| Torque transducer |
| Boot |
| Literature |
| Computing resources |
|---|
| CVS |
| Ethics |
|---|
| SDS / Inventory |
|---|
Servo-valve module
Schematic
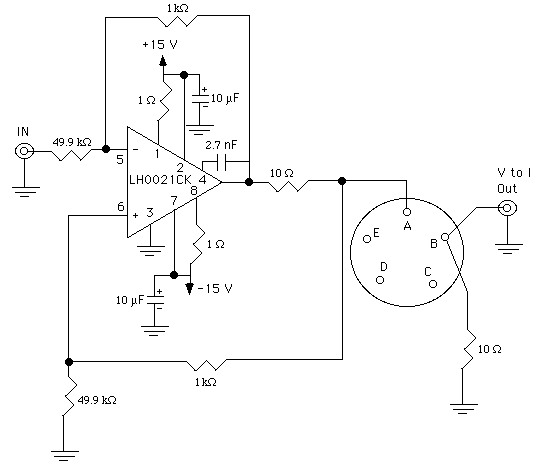
The components used in this module are:
- LH0021CK operational amplifier
- Capacitors
- Resistors
- Cannon connector
- BNC connector
Functional description
faceplate.cdr: CorelDRAW 9.0 file used to make faceplates
This module is a voltage-to-current converter that is used to drive the servo-valve. The input voltage to this module comes from the transputer and is controlled by the desired output position of the actuator (remembering that 0.1 rad=1 volt) and the servo gain. All these parameters are set in the ankle_gui in Matlab.
This input voltage is then converted to current in the servo-valve module based on the transfer function of the circuit, which is Iout/Vin=2mA/V. To determine how much current will drive the servo-valve, take this simple example. We want to displace the actuator by 0.1 rads and set the servo gain to 1. Therefore 1 volt is input to the module and 2mAmps will drive the servo-valve to move the actuator 0.1 rads.
The servo valve is connected across pins A and B of the cannon receptacle. The current that drives the servo-valve also flows through the 10 ohm resistor connected to ground. The voltage across this resistor is output via the V to I BNC and is V=Iservo*R=Iservo*10. Therefore, Iservo=V/10.
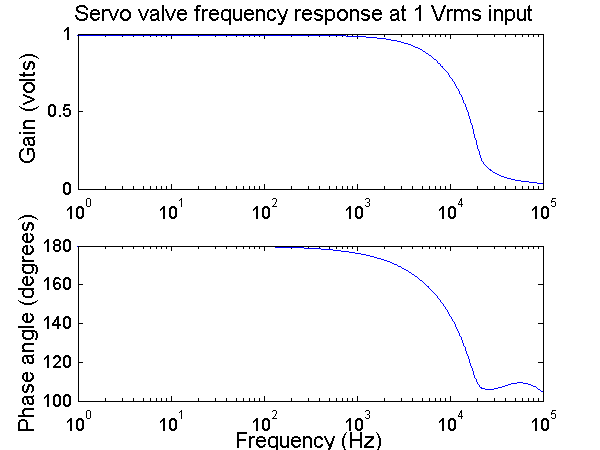
Frequency response
The frequency response at a Vrms of 1 and 10 produce a gain at 1 with a roll off at 1KHz. The phase is 180 during the pass region and rolls off in the transition region.
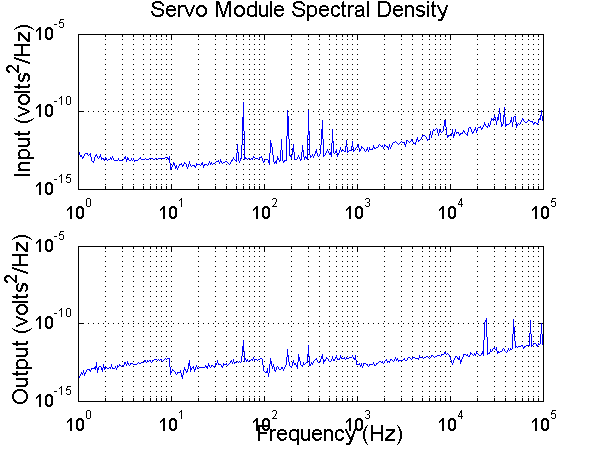
Noise analysis
The noise analysis to a 0 volt input shows that the module produces very little noise.
Last modified: November 14, 2001 Laura Galiana